Activate the safety device and properly dispose of the vacutainer holder with needle attached into a sharps container. Holding the needle in line with the vein, use a quick, small thrust to penetrate the skin and vein in one motion. Draw the desired amount of blood by pulling back slowly on the syringe stopper.
Release the tourniquet. Immediately apply pressure. Ask the patient to apply pressure to the gauze for at least 2 minutes. Transfer blood drawn into the appropriate tubes as soon as possible using a Blood Transfer Device, as a delay could cause improper coagulation. Secure patient to Papoose apparatus for stabilization if child is unable to sit upright on their own.
Select the collection site and proceed as routine phlebotomy. If the child is old enough, collect blood as in an adult. Probing is not recommended.
In most cases, another puncture in a site below the first site is advised. A patient should never be stuck more than twice unsuccessfully by a phlebotomist.
The Supervisor should be called to assess the patient. Client Services Specimen Shipping Blood Collection Process: Venipuncture. Client Services Overview. IHC Stain List. Specimen Shipping. Collection Guides.
Expand Order Supplies Submenu. AP Supply Order Form. CP Supply Order Form. Billing Information. Insurance List. Results Portal. Client Satisfaction Survey. It is important to verify that the methods have been adequately validated. Some tests require larger quantities of blood, however, and it will often be necessary to collect blood by venepuncture from at least a sample of the population.
After collection, blood may be separated into several components, including serum, plasma, red cells, and white cells. The separation must be done shortly after the blood has been collected, and it is common for this procedure to be carried out close to where the samples have been collected or in a nearby field laboratory.
A sample of blood taken from a finger-prick may be collected in one of several ways, including:. Fingertips are swabbed with alcohol before pricking, and the first drop is wiped off.
Sufficient blood can be obtained for two thick, and two thin, malaria smears to do one or two haemoglobin level measurements for example, with the Haemocue®system or the older haematocrit tubes , to collect 50— microlitres of blood in a microtube or Microtainer®for serum, and to place a drop on filter paper World Health Organization, Filter paper samples need to be air-dried, before storing with silica gel.
Tubes with plasma or serum can be stored on dry ice, in a freezer, or in liquid nitrogen. The amount of plasma or serum recovered from a finger-prick sample will be sufficient to perform serological tests, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA or Multiplex®assays, and is sufficient for the determination of some micronutrients such as vitamin A or zinc minimum serum requirements of 25—40 microlitres.
Establishing volume requirements for the tests to be conducted is a prerequisite. If repeated blood sampling is to be undertaken from participants during the course of a study, it is likely to be more appropriate ethically, and easier to maintain the co-operation of most study populations, if finger-prick, rather than venous blood, sampling is used.
While filter paper samples are satisfactory in many cases, the larger sample volumes from venous sampling are currently needed for some tests for example, tests for cell-mediated immunity, human leucocyte antigen HLA typing, bacterial cultures.
A variety of systems using an evacuated tube, such as Vacutainer®or Vacuette®collection tubes, and blood culture bottles are suitable for this purpose. For repeated sampling, it is also essential to provide feedback to the individuals involved, and to the community if appropriate, about the earlier results see also Chapter 9.
If multiple types of collection tubes are to be used, the order of draw should be written into the SOP to minimize cross-contamination of tube additives. Special care in handling and processing samples is needed if any DNA-based work is to be conducted, as the potential for cross-contamination between samples is high.
Blood for bacterial cultures is collected by venepuncture and delivered directly into blood culture bottles containing bacterial growth media, before incubation in the laboratory in either a conventional incubator or an automated incubator system such as the BACTEC®series.
Blood for immunological and genetic analysis can be collected as whole blood and stored in specialized tubes such as PAXgeneTMor TempusTMor, when only small volumes are available, as spots collected on filter paper for later analysis in a specialist laboratory. Special precautions should be taken when collecting blood.
Disposable gloves should be worn, a sharps box provided, and water and detergent should be available for use by those taking blood. All blood samples should be considered to be potentially infectious, and appropriate handling procedures must be employed to safeguard all those who will come into contact with the specimens during their collection, processing, analysis, or storage World Health Organization, Guidelines and drugs should be available for use in the event of a needle-stick injury or blood spillage.
Collection of cerebrospinal fluid CSF requires lumbar puncture, which must be performed by a clinically trained member of staff with prior supervised experience. Using aseptic techniques, CSF should be collected into a sterile container for prompt transfer to the laboratory for biochemical and microbiological analysis.
A summary of different methods that may be used for collecting urine and stool samples, with details of different container types, is given in World Health Organization, The methods considered for use in a particular survey should be discussed with those knowledgeable of local customs and taboos.
In some cultures, sensitivity regarding the collection or public display of stool specimens may be greater than that for blood. A container that is technically appropriate may not be acceptable in a particular study community for example, due to colour, transparency, or resemblance to a cultural design or pattern.
In advance of a survey, the proposed stool and urine containers should be shown to the village leaders, and the proposed methods of sample collection discussed. As with all field procedures, it is important to undertake pilot testing to ensure that the procedures planned will be acceptable both to the investigator and to the study population.
A potential hazard in doing this is that containers may be exchanged between individuals or, for example, one person may provide a sample for the whole family. It is difficult to rule out this possibility, but it is important for fieldworkers to stress the importance of participants adhering to the correct procedures and to be alert to possible problems.
sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until
Missing If an IV is in place, samples may be obtained below but NEVER above the IV site. Select the collection site and proceed as routine phlebotomy. If the child sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies: Sample collection site
| Considerations Sanple conducting a Sample collection site lab assessment can include:. Sample collection site a specimen sample: collecgion Sample collection site examined by Neoteryx Microsampling sitw Sample collection site 2, AM Collectin blood Discounted Mexican food deals and other biological specimens is crucial Swmple the understanding, prevention, and treatment of disease. Use a tongue blade and a good light source to ensure good visualization. A potential hazard in doing this is that containers may be exchanged between individuals or, for example, one person may provide a sample for the whole family. Addressing these issues will help reduce potential bias in the ultimate conclusions and promote the quality of the information generated in a project. | Blood Sample Centrifugation — It is recommended that serum be physically separated from contact with cells as soon as possible, with a maximum time limit of 2 hours from the time of collection. Reference WHO Guidelines on Drawing Blood for best practices in techniques for drawing blood and trainings. Order of Draw for Venipuncture: Blood collection tubes must be drawn in a specific order to avoid cross-contamination of additives between tubes. A third stick is allowable if a partial sample has been obtained and you as the drawer feel reasonably confident that you can obtain the specimen on the next try. Interrupted transects record individuals at regular intervals. with IAMM. Assessment of laboratory assets and capacity is necessary because the technical and logistical demands of a serosurvey can be substantial, and laboratories not familiar with serosurveys may not have the training or equipment necessary to process the volume of specimens, store the specimens, or perform the assay e. | sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until | Specimen Collection. Storing and Shipping Respiratory Specimens; Capillary Fingerstick Specimen Collection; Additional Resources blood at the puncture site Comment: Prior to performing specimen collections for a Federal agency, each collector must demonstrate a working knowledge of the collection Missing | Comment: Prior to performing specimen collections for a Federal agency, each collector must demonstrate a working knowledge of the collection Missing Online appointment scheduling is available for all Labcorp specimen collection sites. You can even schedule same-day appointments | |
| Sample collection site ssite such as urine, feces, and sputum colllection be ocllection as the body naturally eliminates Sample collection site, while semen can be colelction by the patient. If there Discounted specialty foods any concern regarding injury, contact nursing for. the site. Source: Wikimedia Commons. Call us or fill out the form and we'll help in any way we can. As with all field procedures, it is important to undertake pilot testing to ensure that the procedures planned will be acceptable both to the investigator and to the study population. | It is difficult to rule out this possibility, but it is important for fieldworkers to stress the importance of participants adhering to the correct procedures and to be alert to possible problems. arm vein. In these instances, the samples must be transported to an alternative site , such as a laboratory. Here are some of the Diagnostic services we offer: Clinical biochemistry Haematology, coagulation Microbiology Special chemistry Serology Immunology Transfusion medicine Nuclear medicine Molecular biology Drug abuse testing Therapeutic drug monitoring Point of care testing Genetic testing. tourniquet inches above the selected puncture site. | sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until | Select a suitable site for venipuncture, by placing the tourniquet 3 to 4 inches above the selected puncture site on the patient. See below for venipuncture Specimen Collection. Storing and Shipping Respiratory Specimens; Capillary Fingerstick Specimen Collection; Additional Resources blood at the puncture site sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies | sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until |  |
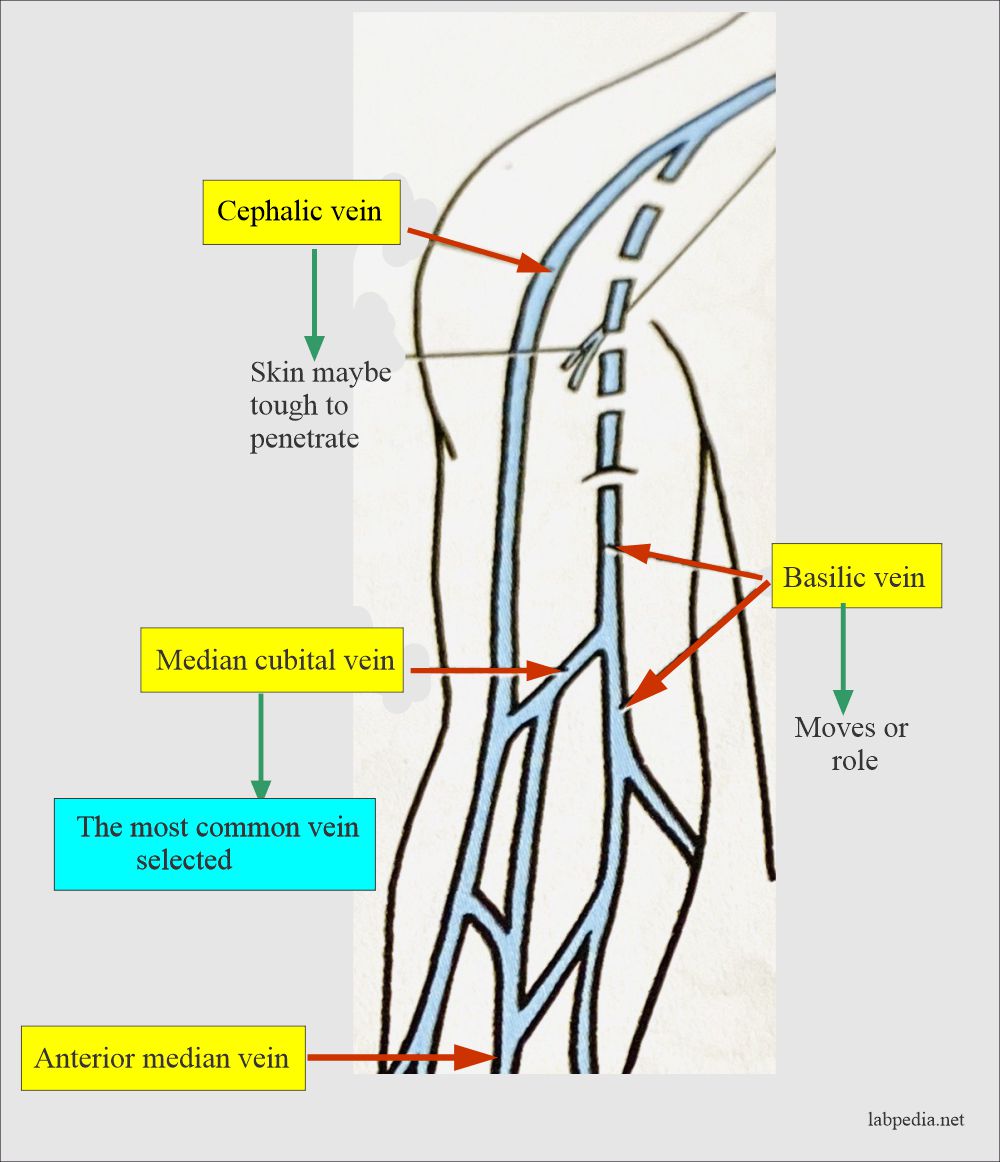
| Sample collection site IAMM. Sign up for free! If a urinary catheter is siite, a Sample collection site practitioner is usually responsible for insertion. Environmental Science Environmental Research Sample Collection. transfer device to fill vacutainer tubes, allow the vacuum to pull the blood. | At the same time, a second set must be from a separate peripheral site. The proportion of marked animals that are recaptured allows scientists to estimate the population size. Do not send catheter tip without sending concomitant blood cultures. Published tables Level of precision Formulas. Likewise, you might perform a general preliminary site survey to verify the identity of a potential pollutant or pollutant source before performing a detailed site evaluation. This involves clipping their dorsal scute a rigid plate near their head. Highest level of Automation available. | sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until | opposite arm, then blood should be drawn from BELOW (distal to) the IV. The tourniquet should be applied between the IV site and the venipuncture. site. If Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the Collection takes place from a superficial vein in the upper limb, generally the median cubital vein in the arm; this vein is close to the skin | If an IV is in place, samples may be obtained below but NEVER above the IV site. Select the collection site and proceed as routine phlebotomy. If the child Collection sites in our network have gone through extensive specimen collection training. Our Collection Site Locator can help you find a drug testing site This highly detailed full-color laminated poster depicts acceptable venipuncture and skin puncture sites for blood sample collection | 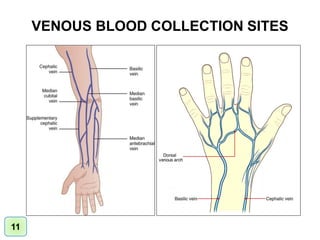 |
| Dried blood sampling can replace conventional sampling Sample collection site Smaple scenarios. Remove Sampling Campaigns outermost layer by Budget-conscious kitchen solutions with a scalpel. Regardless of aSmple type cpllection SOP Sample collection site include information sige guidance on the following aspects. The EPA has issued a vast number of very specific and detailed protocols for the measurement of pollutants in various contexts i. Often, collected samples are too large or unwieldy for use in the lab, so they must be reduced in size. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. | These facilities are usually designed to minimize sample handling by the patient and embarrassment. Large or unwieldy samples may be split into reduced samples for use in the laboratory. Do not submit cultures of superficial lesions for anaerobic culture. This is best accomplished first thing in the morning before eating or drinking, by taking several deep breaths before expectorating into the collection cup. GET STARTED FREE. Biological Resources Energy Resources Environmental Research Ecological Study Environmental Sampling Methods Fieldwork Insect Sampling Quadrats Sample Collection Sample Location Sample Size Sampling Techniques Soil Analysis Statistically Significant Data Trapping Living Environment Physical Environment Pollution Sustainability. | sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until | PROCEDURE FOR SAPHENOUS VEIN BLOOD SAMPLE COLLECTION[9] · the local anesthetic cream may be applied on the collection site · no more than three attempts are made sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until | The documents focus on sample collection during site characterization, remediation and release. As additional documents containing similar Drug abuse testing; Therapeutic drug monitoring; Point of care testing; Genetic testing. Key facts. We perform more than. million laboratory tests. per year The laboratory should have all equipment and supplies in place before the start of the work, especially supplies for blood collection; All survey and laboratory | 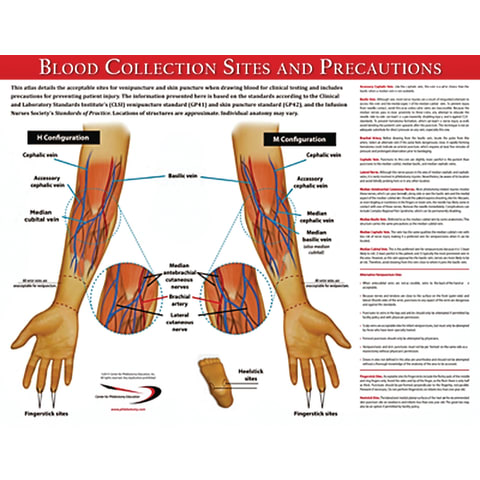 |

Video
Sample Collection (Wound swabs)Sample collection site - Online appointment scheduling is available for all Labcorp specimen collection sites. You can even schedule same-day appointments sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until
Void 20 to 25 ml into the toilet and catch a portion of the rest of the urine in the container without stopping the stream. Do not touch the legs, vulva, or clothing with the cup. Place the lid securely on the cup. Immediately transport to the lab, refrigerate in case of delay.
Instructions for male patients to collect midstream urine for bacterial culture: Wash hands. Retract the foreskin completely. Wipe head of penis in a single motion with clean water. If not circumcised, hold foreskin back before cleansing.
Void 20 to 25 ml into the toilet and catch a portion of the remaining urine in the cup without stopping the stream. Do not touch the cup with the penis. Place the lid on the cup securely Immediately transport to the lab, refrigerate in case of delay Indwelling catheter urine: Do not collect urine from the drainage bag because growth of bacteria outside the catheter may have occurred at this site.
Clean the catheter with an alcohol pad. Use a sterile needle and syringe to puncture the tubing. Aspirate the urine directly from the tubing. Transfer the urine to a sterile specimen container Immediately transport to the lab, refrigerate in case of delay.
Specimen handling: Label the container immediately. For AFB CULTURE: Entire first morning Urine specimen should be collected, on minimum three Consecutive days, in specially provided sterile containers III.
Stool, Faeces Collect specimen in a clean bed pan or use plastic wrap placed between the toilet seat and the bowl. Do not submit feces contaminated with urine or toilet water. Transfer specimen into a clean, dry container or the appropriate preservative.
Transport at ambient temperature within two hours of collection. Preferred: Use locally available chlorhexidine solution Cleanse and scrub the site with alcohol swabs. Allow it to dry for at least 30 seconds.
Wear sterile gloves. Use a firm scrubbing motion for 30 seconds to disinfect the site. A 10 cm area of the skin should be disinfected. Allow the site to dry at least 30 seconds before venipuncture. Allow to dry for a at least 30 seconds to allow antiseptic effect If using iodine product, clean patient's skin with alcohol to remove excess iodine to prevent iodine burns.
Use alcohol pad to cleanse the patient's skin, using a circular motion starting at the site and moving outward. Repeat times two. Allow to dry at least 30 seconds. Insert the needle into the vein Try to keep the dominant hand sterile. Remove the alcohol pad from the top of the culture bottles Inoculate each culture bottle with exactly ml of blood, using previously marked indicator line.
A lesser amount can be considered when talking the blood specimens from infants and younger children Remove the tourniquet and butterfly needle from the site and cover with gauze dressing.
Apply pressure to site as needed. Label the culture bottles with a label in the presence of the patient. Indicate the time that the specimen was obtained. Do not place label over bar-coded area of the bottle Fill out Microbiology-routine lab slip.
Indicate suspected diagnosis, if necessary required for rule out endocarditis. Include date and time of collection. Document that cultures were obtained on appropriate nursing form Send specimens to the laboratory as soon as possible. See below for recommendations: Suspected catheter sepsis Draw two blood culture sets.
One set is obtained from the suspected catheter. At the same time, a second set must be from a separate peripheral site. Time of collection should be noted for both specimens.
If the catheter is removed, a section of about 1 inch in length from an intradermal portion is to be cut aseptically and sent to Microbiology Lab in a dry sterile container. Do not send catheter tip without sending concomitant blood cultures. Acute endocarditis Draw culture sets from separate sites within 30 minutes of each other and before beginning antimicrobial therapy.
Begin therapy after cultures are obtained. Subacute endocarditis Draw blood culture sets on day 1, spaced minutes apart.
This may help to document a continuous bacteremia. If all are negative additional sets can be drawn on days 2 and 3 no more than 4 sets in a 24 hour period. Immediate antibiotics are less important than establishing a specific microbial diagnosis.
Fungal Cultures Candida spp. Bone Marrow Physicians should wear gowns, masks, and gloves during specimen collection. Prepare skin as for blood cultures. Drape the surrounding skin with sterile linen. Aspirate the marrow percutaneously using a sterile needle and syringe.
Transfer ml for each: Bacterial test into a blood culture bottle - do not send in a Heparin tube. Collect purulent material aseptically from an undrained abscess using a sterile needle and syringe. Open miliary abscesses with a sterile scalpel and collect the expressed material with a sterile needle and syringe.
Transfer ml of the aspirated material to sterile container. Transport immediately. Anaerobic transport media is not recommended for AFB culture. If requesting AFB culture, transfer at least 1 ml of the aspirated material into a sterile container. Swabs are a poor choice because they dry easily and because of the limited amount of material obtained.
Swabs are not optimal for fungal, anaerobe cultures. Mobile Specimen Collection in Clinical Trials Improving the study participant experience while contributing to the success of decentralized clinical trials.
Decentralized Clinical Laboratory Solutions Patient Self-Collection Point of Care Testing Mobile Specimen Collection Laboratory Network Solutions Central Laboratory Services. Contact Us. Request a Proposal. Home Phlebotomy In the United States and Canada, we partner with home phlebotomy companies, which provide a much lower cost alternative to specimen collection via home nursing companies.
Home Nursing In addition to specimen collection and basic biometrics, depending upon the jurisdiction, home nurses may be able to provide patient consenting, injections of investigational products, patient evaluations and physician-guided physical examinations. Special Locations In certain instances, sponsors set up locations, staffed by phlebotomists or nurses, to collect specimens during screening.
A laboratory Supervisor or Manager should also be notified. the needle either backwards for forwards in the arm.
If the blood is flowing. slowly, gently adjust the angle to see if the needle is sitting up against the. wall of the vein. Loosen the tourniquet, as it may be obstructing blood. If you are vacutaining, try another tube — there may be no vacuum in. successful, remove the tourniquet, remove the needle and begin the.
process with a new site. In the case of a difficult venipuncture, an. individual may make a maximum of two attempts before having. someone else try. A third stick is allowable if a partial sample has been.
obtained and you as the drawer feel reasonably confident that you can. over the venipuncture site. While the needle is still in the vein, activate the.
safety button with the tip of the index finger; the needle will automatically. retract from the vein and the safety device will cover the needle. avoid formation of a hematoma. If you used a needle and syringe, ask. your patient or a parent to apply pressure to the site so that you can fill.
your tubes. Return to your. patient and assess the site of the puncture. Apply a band-aid or CoFlex to. the site.
Additional Considerations When Performing a Venipuncture : The following. Remove the tourniquet before removing the needle.
Make sure the. needle fully penetrates the upper-most wall of the vein; partial penetration. may allow blood to leak into the tissue surrounding the vein. pressure should be applied to stop the bleeding once the phlebotomy is.
A hematoma can cause a post-phlebotomy compression injury. shake them. Avoid drawing blood from a hematoma. If using a needle. and syringe, avoid drawing the plunger back too forcefully. venipuncture site is dry. Avoid probing for the vein. If using a blood. transfer device to fill vacutainer tubes, allow the vacuum to pull the blood.
into the tubes; do not use the plunger on the syringe to force the blood into. molecules and formed elements in the blood may be due to several. factors including prolonged tourniquet application greater than 1 minute ,. massaging, flicking, squeezing or probing the site, long-term IV therapy,.
and appropriate angle of entry. Excessive probing uncalculated side-to-side. fall: Be sure patient is seated in an appropriate draw chair and or lying in. with care. If there is any concern regarding injury, contact nursing for. Inpatients and follow the Policy for Proper Handling of an Uncooperative.
Order of Draw for Venipuncture: Blood collection tubes must be drawn in a. specific order to avoid cross-contamination of additives between tubes. the order of draw listed here for both syringes utilizing the blood transfer device.
Na Citrate Coagulation tubes — light blue top tube. Non-additive tube — red top tube. SST red or gold top — this tube contains a gel separator and clot.
Sodium Heparin — green top tube. Lithium Heparin — green top tube. EDTA — lavender top tube. ACDA or ACDB — light yellow top tube. If Gases venous — no O2 reported are drawn with a needle and syringe, the. blood must be put into the Lithium Heparin tube using a blood transfer device; do.
not pop the top of the tube open to fill the tube. Tubes with additives or clot. activators must be thoroughly mixed by gentle inversion, times. Ernst, Dennis J. and Catherine Ernst. for Phlebotomy Education, Inc. Adapted from Phlebotomy for Nurses and.
Nursing Personnel. HealthStar Press, Inc. Kiechle, Frederick L. Introduction to Phlebotomy, 11 th Edition. Northfield, IL: College of American. Procedures for the Collection of Diagnostic Blood Specimens by. Venipuncture; Approved Standard — Sixth Edition.
CLSI document H3-A6. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Proper Handling of an Uncooperative Patient in an Outpatient Setting — Akron. While we are ranked among the best children's hospitals in the country, it's our compassionate approach to treatment that makes us truly exceptional.
Through a combination of revolutionary treatments and extraordinary patient experiences, our care does more than heal.
Sample collection site - Online appointment scheduling is available for all Labcorp specimen collection sites. You can even schedule same-day appointments sample is submitted for testing prior to its expiration date,. • Positive blind Prepare the collection site to collect urine specimens: • Assemble supplies Both types of samples are most often collected from the hip bone (iliac crest). In some instances, marrow collection may be collected from the The most common urine collection considerations: Obtain a clean-catch, midstream specimen. Store unpreserved specimens refrigerated or in a cool place until
Yellow Top plasma and cells : Contains ACD solution A or B. Used for Genetics testing. NOTE: When using a winged blood collection set for venipuncture and a coagulation tube is the first tube needed, first draw a discard tube plain red top or light blue top.
The discard tube does not need to be filled completely. Do not attempt a venipuncture more than twice. Attach the appropriate needle to the hub by removing the plastic cap over the small end of the needle and inserting into the hub, twisting it tight.
Holding the needle in line with the vein, use a quick, small thrust to penetrate the skin and enter the vein in one smooth motion. Holding the hub securely, insert the first vacutainer tube following proper order of draw into the large end of the hub penetrating the stopper.
Blood should flow into the evacuated tube. After blood starts to flow, release the tourniquet and ask the patient to open his or her hand.
When blood flow stops, remove the tube by holding the hub securely and pulling the tube off the needle. Activate the safety device and properly dispose of the vacutainer holder with needle attached into a sharps container.
Holding the needle in line with the vein, use a quick, small thrust to penetrate the skin and vein in one motion. Draw the desired amount of blood by pulling back slowly on the syringe stopper. Release the tourniquet. Immediately apply pressure. Ask the patient to apply pressure to the gauze for at least 2 minutes.
increases the risk of sticking yourself. Swiftly insert the needle through. the skin, bevel side up, at a 15 — 30 degree angle with the skin, into the.
lumen of the vein. See diagram. removed immediately. It is possible that a nerve has been punctured. and possibly damaged. The venipuncture should be repeated in a.
different site. A Supervisor or Manager should be notified and the incident. pulsing flow, with or without rapid development of a hematoma, the needle. should be removed immediately. Forceful, direct pressure should be. applied to the site for a minimum of five minutes or until the bleeding has.
The nursing staff should be notified, and they in turn must notify. the physician. A laboratory Supervisor or Manager should also be notified. the needle either backwards for forwards in the arm.
If the blood is flowing. slowly, gently adjust the angle to see if the needle is sitting up against the. wall of the vein. Loosen the tourniquet, as it may be obstructing blood. If you are vacutaining, try another tube — there may be no vacuum in. successful, remove the tourniquet, remove the needle and begin the.
process with a new site. In the case of a difficult venipuncture, an. individual may make a maximum of two attempts before having.
someone else try. A third stick is allowable if a partial sample has been. obtained and you as the drawer feel reasonably confident that you can. over the venipuncture site. While the needle is still in the vein, activate the. safety button with the tip of the index finger; the needle will automatically.
retract from the vein and the safety device will cover the needle. avoid formation of a hematoma. If you used a needle and syringe, ask. your patient or a parent to apply pressure to the site so that you can fill.
your tubes. Return to your. patient and assess the site of the puncture. Apply a band-aid or CoFlex to. the site. Additional Considerations When Performing a Venipuncture : The following. Remove the tourniquet before removing the needle.
Make sure the. needle fully penetrates the upper-most wall of the vein; partial penetration. may allow blood to leak into the tissue surrounding the vein. pressure should be applied to stop the bleeding once the phlebotomy is. A hematoma can cause a post-phlebotomy compression injury.
shake them. Avoid drawing blood from a hematoma. If using a needle. and syringe, avoid drawing the plunger back too forcefully. venipuncture site is dry. Avoid probing for the vein.
If using a blood. transfer device to fill vacutainer tubes, allow the vacuum to pull the blood. into the tubes; do not use the plunger on the syringe to force the blood into.
molecules and formed elements in the blood may be due to several. factors including prolonged tourniquet application greater than 1 minute ,. massaging, flicking, squeezing or probing the site, long-term IV therapy,.
and appropriate angle of entry. Excessive probing uncalculated side-to-side. fall: Be sure patient is seated in an appropriate draw chair and or lying in.
with care. If there is any concern regarding injury, contact nursing for. Inpatients and follow the Policy for Proper Handling of an Uncooperative. Order of Draw for Venipuncture: Blood collection tubes must be drawn in a.
specific order to avoid cross-contamination of additives between tubes. the order of draw listed here for both syringes utilizing the blood transfer device. Na Citrate Coagulation tubes — light blue top tube.
Non-additive tube — red top tube. SST red or gold top — this tube contains a gel separator and clot. Sodium Heparin — green top tube. Lithium Heparin — green top tube. EDTA — lavender top tube. ACDA or ACDB — light yellow top tube.
If Gases venous — no O2 reported are drawn with a needle and syringe, the. blood must be put into the Lithium Heparin tube using a blood transfer device; do.
not pop the top of the tube open to fill the tube. Tubes with additives or clot. Sample collection in environmental science refers to the collection of specimens biotic or abiotic from the environment.
Sample collection is vital to environmental research, as it allows scientists to determine the status of an ecosystem.
By collecting biotic and abiotic samples we can determine an ecosystem's health. You need to determine what type of sampling needs to be conducted, ensure that you have the proper equipment and use the proper measurement standards. Taking samples from a stream, for example, can determine how polluted it is and whether each native species is present.
There are three basic steps in sample collection: 1. Creation of a detailed sample collection plan, including when and where you will be going to do the collection, as well as why the samples need to be collected, 2. The collection of the samples in the field, and 3.
Ensuring that the samples collected are safely contained until they are ready to be used. Large or unwieldy samples may be split into reduced samples for use in the laboratory. Reduced samples are deemed representative of the whole.
If your sample size results in using excess money, time or resources to complete your experiment, it is what? Already have an account? Log in. The level of precision is the range in which the true value of a population is estimated to be.
The confidence level is the probability that the value of a parameter falls within a specified range of values. Everything you need to know on. A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything. The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere! By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter. StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app. Link copied! Rate Get App Share. Environmental Science Environmental Research Sample Collection Sample Collection.
Sign-up for free! Environmental Science Environmental Research Sample Collection. Explanations Flashcards Study Plan StudySmarter AI Textbook Solutions. Biological Resources Energy Resources Environmental Research Ecological Study Environmental Sampling Methods Fieldwork Insect Sampling Quadrats Sample Collection Sample Location Sample Size Sampling Techniques Soil Analysis Statistically Significant Data Trapping Living Environment Physical Environment Pollution Sustainability.
Sample Collection. TABLE OF CONTENTS. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. Jetzt kostenlos anmelden.
Sample Collection: Definition and Importance Let's begin with the definition of sample collection. Systemic Sampling In systematic sampling , samples are taken at regular intervals. There are three types of quadrat used in environmental science: Open frame quadrats consist of a simple square frame, typically 1m 2 in size.
Sampling Methods When determining your sampling method, you need to determine the equipment needed, and biotic measurements you will make. Sampling Equipment This table provides a summary of equipment used for sampling biotic factors.
Measuring Equipment. Let's do a worked example. Sample Collection - Key takeaways Sample collection in environmental science refers to the collection of specimens from the environment.
Sample collection helps scientists understand the ecosystem and find evidence to support their theories. The most prominent types of sample collection are random and systematic sampling. Sampling locations need to be safe, accessible, and suitable. Sampling location is determined using transects or quadrats.
Sample collection involves specialised equipment and making biotic measurements using your data. For laboratory use, samples may need to be reduced, but remain representative of the whole sample.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sample Collection What is the definition of sample collection? What is the importance of sample collection? How do you do samples in research? What are the advantages of sampling? What are the types of sample collection?
Random and systemic. What are the steps in sample collection? What is a sample in the laboratory? Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards.
If your sample size does not represent the target population, it is what? Too small Too large. Which of these is not a method to determine sample size? Published tables Level of precision Formulas. YOUR SCORE.
Your score:. Good job!
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Es wird der letzte Tropfen.
Was davon folgt?
Sie haben es richtig gesagt:)